|
Afedri LAN-IQ
Alexander Trushkin (4Z5LV) has been
developing and producing SDR receivers since 2012. These are offered
under the "Afedri" brand on its
website. Afedri means:
Analog
Front-End
Digital
Radio
Interface
and refers to the DDC chip Afedri8201 from Texas Instruments.
Block diagram of the LAN-IQ The LAN-IQ works from 30KHz - 35Mhz as a direct sampler and from 35MHz - 1700MHz as a tuner-based SDR with the well-known R820T2 chip.
Peculiarities in standalone operation In standalone mode, the LAN-IQ has a few special features that I will briefly discuss here. A Y-USB cable is supplied with the LAN-IQ. This is required if the device is operated on USB2. If the LAN-IQ is operated with large sample rates, it needs about 850mA. Because a USB2 connection only supplies 500mA, the LAN-IQ is then undersupplied and could not function properly. With this Y-cable you can use 2x USB2 sockets and then have 1000mA available. Of course, this also applies if the LAN-IQ is controlled via the PC. The best thing is to use a USB3 connection or an external low-interference 5V power supply. The device also has a hollow socket for power supply. This can be used to apply a voltage of 7-10V. Unfortunately, it turned out that the LAN-IQ gets very warm if you feed it through the hollow socket. This is due to the voltage converter, which regulates down to 5V. Basically I recommend to supply the LAN-IQ with voltage via the USB connection. Ideally, the LAN-IQ is operated with the supplied stylus. The touchscreen can of course also be operated with your bare fingers. Then you make a typing mistake very quickly because the typing areas are small. You can quickly find out that if you swipe the lower spectrum over the display, the frequency can be adjusted with the previously selected tuning step. In the upper waterfall display, tap on the display to set the desired frequency. The tap does not set the frequency in the selected step size, but in 1 Hz steps. Use the "Step + & Step-" buttons to set the step size. The step sizes are not as usual as with a wideband receiver. Each press of the step buttons increases or decreases the step size by a factor of 10. This makes it difficult to set a frequency precisely. Also because the set tuning step is not rounded. The exact setting of a frequency is possible with the direct input via the numeric keypad which can be activated by pressing the frequency display or "Mod." can call. The AM operating mode was somewhat neglected. The bandwidth filters sometimes have unusual values and the AGC cannot be set. There is no adjustable AGC in SSB either. You don't have the option to choose between AGC "Fast - Medium - Slow". AGC control is certainly present, but it is too fast. That is why the LAN-IQ rushes up quickly during the speak breaks. This is somewhat reminiscent of the JRC NRD-545 DSP, which also had no adjustable AGC in AM. The other special feature of the LAN-IQ in standalone mode is the programming and operation of the 100 frequency memories. The LAN-IQ has memory banks in which only defined frequencies can be stored. The memory contents must be called up individually by entering the memory location number. It is not possible to scan the memory in the current firmware version, which makes working with the memory functions very difficult.
Memory 0-13 are
reserved for amateur radio frequencies. Frequencies outside the
amateur range are not saved. All other functions can be easily mastered by the experienced operator. In the pictures below you can see that my LAN-IQ has a tuning knob to the left side of the display. This is not self-made, but can be ordered as an option. However, the manufacturer (Alex) advises against choosing this optionMemory! The problem with this option is that the encoder used is mechanical and does not have a long lifespan. It is also important to note that this option is excluded from the guarantee. My LAN-IQ also has a stand to put it in a comfortable working position. I installed this stand myself and is not included in the scope of delivery.
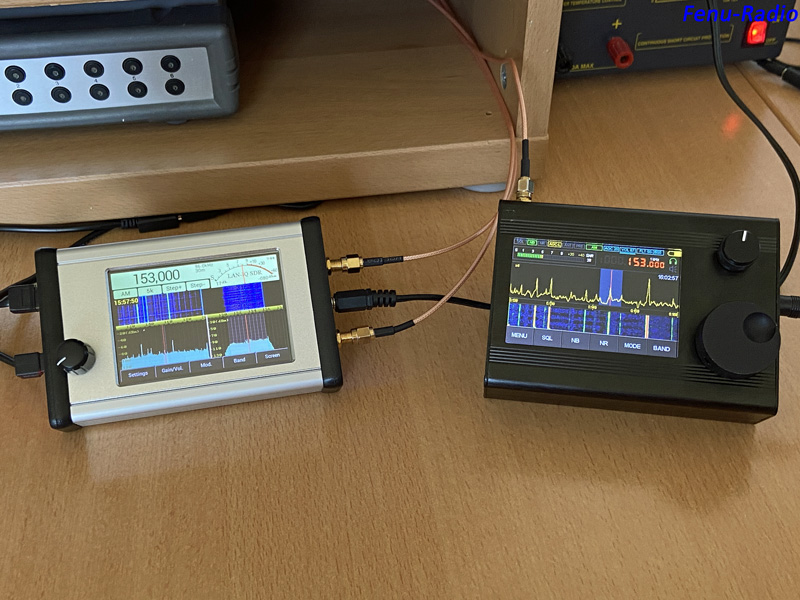
LAN-IQ in standalone mode
With the built-in
touch display, the LAN-IQ can also be operated without a computer.
Due to the small display dimensions, working with the LAN-IQ is a
bit fiddly. But if you use the supplied stylus as an aid, you will
get along well with the device after a little getting used to it.
While browsing the Internet, I came across an option that the
manufacturer of the LAN-IQ does not offer directly. Some LAN-IQ
devices, allegedly not all, are prepared for the installation of a
tuning encoder. On the board on which the display is mounted, there
is a place where you can install a mechanical encoder. Upon request,
an encoder was installed in my LAN-IQ. Unfortunately, the joy didn't
last long. The encoder used is not suitable because it have detents.
The reason for this is that each detent gives two impulses. This
means that the frequency changes by two steps per detent.
Fortunately, I still had Bourns encoders of the same type from an
old project. These had no detents. I immediately replaced the
encoder. And lo and behold, it works perfectly!
The LAN-IQ can be seen in operation in the video. For standalone operation there is a headphone or an active speaker. In this case the active speaker Bose Soundlink Mini II. It gives the somewhat thinny sounding LAN-IQ a little more sonority. The LAN-IQ can also decode digital operating modes. That means RTTY, PSK and QPSK. Unfortunately, only baud and shift rates for amateur radio operation are available. Pity! In the video from minute 6:10 you can see how the LAN-IQ copes with it. Decoding works well once you have found a station.
LAN-IQ as a portable SDR With its concept, the LAN-IQ still offers the possibility of portable use. With a good 5V power bank, the LAN-IQ can be operated outside of the shack for many hours. My power bank has 10400mAh and easily hold 10 hours. The MLA30 active loop is also connected to it.
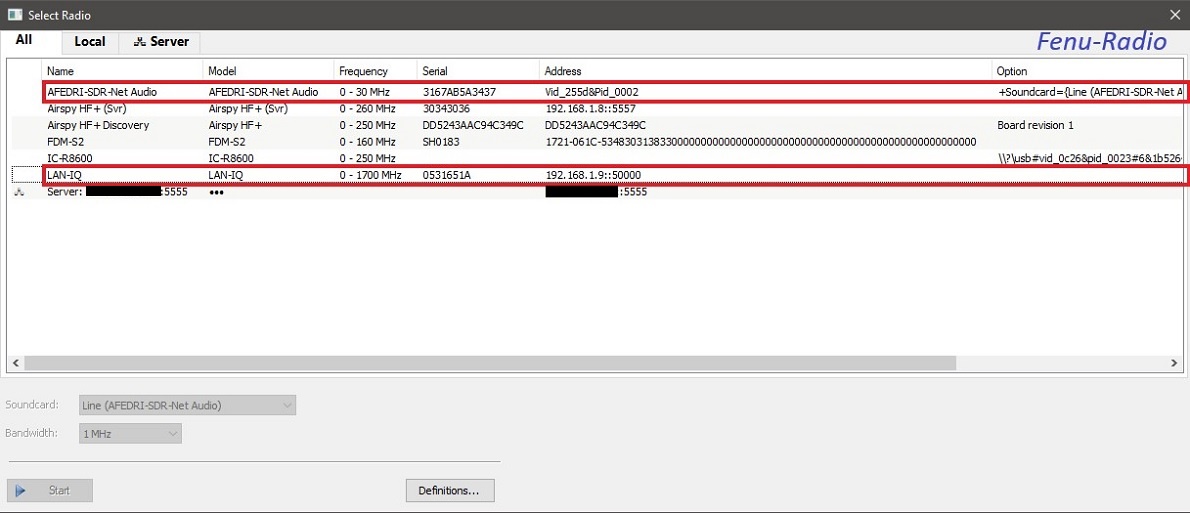
LAN-IQ in PC mode The LAN-IQ can be connected with the PC in two ways. Either via USB2 or via the LAN connection. If you operate the LAN-IQ via USB2 you quickly determine that the spectrum bandwidth with max. 250KHz. Dependent from the sound card of the PC. The LAN connection belongs for significantly more bandwidth. This allows up to 2MHz bandwidth up on the monitor. If you choose LAN operation, you have two functions to connect to the network. You can connect the LAN-IQ directly to the network card of the PC, or you can connect it to a router. If you go through the router, you have the option of remotely controlling the LAN-IQ via the Internet, because it has a built-in network interface. My device is connect on the router, that simplified the configuration. Choice between USB and LAN connection with the SDR-Console V3.
The LAN-IQ can be operated with many programs. Shown below in operation with the SDR-Console V3, HDSDR in connection with the Afedri Control Box and SDRSharp. SDRSharp offers only support up to 35MHz.
Sensitivity test & audio comparisons The
LAN-IQ is a direct sample SDR with a 12bit ADC from 30KHz - 35MHz.
According to the technical data, it should be quite sensitive. An
MDS of -136dBm (smallest audible signal above the noise) makes you
curious. These are values that the Winradio G33DDC Excalibur Pro
delivers. The following comparisons should show whether it is really
as sensitive as the G33DDC. Antenna compatibility is also an issue.
I use normal hobby antennas like the Datong AD370, the cross loop
with the Reuter amplifier RLA4/2E and a few other antennas. Every
good hobby SDR should tolerate these antennas without complaint. But
now to the comparisons in PC mode!
Differences between the receivers can best be determined with audio comparisons. Of course, this always depends on the settings of the respective receivers. Accordingly, both receivers were set for the best possible reproduction. The noise canceling functions have not been activated. The bandwidth filters and the modulation type were always set the same. The appropriate station was carefully selected so that it could be received as consistently as possible over the recording period so that the differences can also be assessed. It sometimes took several tries. Some recordings are from stations just above the noise floor. I therefore recommend using headphones when listening to the audio comparisons.
Conclusion Standalone operation
The sound differences
from the Malahit DSP are clearly audible. The LAN-IQ rushes
significantly more than its opponent. On the whole, this is not
tragic, but in the long run it is uncomfortable to work with
headphones. This is due to the lack of adjustability of the AGC. The
sound in standalone mode is a bit thin, but understandable. The
antenna compatibility gave no cause for criticism. I was unable to
determine any intermodulations during the entire test period.
Overdrive effects only occurred when the RF gain was turned up fully.
Unfortunately, a few things have not been consistently implemented
by the manufacturer. As a standalone SDR, the LAN-IQ is very
tailored to the radio amateur. You notice this in the operation, in
the underexposed operating mode AM and in the digital operating
modes. I only briefly tested the reception above 35MHz. It receives
well on FM, even in stereo but without RDS. Unfortunately there is
no tuning step for FM radio! The largest tuning step is 10KHz. There
was almost nothing going on in the aeronautical sector due to the
Corona crisis. Nevertheless, the tower from Zurich Airport was
sometimes heard at 118.100MHz. PC operation
The LAN-IQ shines in
PC mode! Its rival, the Winradio G33DDC, has been one of the best
SDRs ever since it was released. The LAN-IQ with its 12bit can
largely keep up. The sensitivity in particular is on par with that
of Winradio. The only differences were in the sound reproduction.
Although the LAN-IQ should receive from 30KHz, the Russian alpha
signals can be received at 11.9KHz. Excellent price / performance ratio! Available from: https://www.afedri-sdr.com/index.php/lan-iq-sdr posted: 01.05.2020
After the first test, which was quite good but revealed a few weaknesses, something happened that only small and flexible companies can manage. The LAN-IQ was updated on a large scale. This update includes a change to the hardware and extensive software updates. When developing the LAN-IQ, a tuning encoder for frequency tuning was never in the focus of the manufacturer, but was offered as an option on request. This was rasterized and mechanical. Unfortunately, the lifespan was not long enough either. It could happen that the mechanical encoder stopped working properly after a few weeks. After the publication of my first test, Alexander Trushkin quickly realized that a tuning knob could be an essential part of the concept and started looking for an optical, high-quality encoder. A suitable optical encoder was found after a few weeks. The search was anything but easy, Alexander reported to me. The required encoder had to be installed in a housing that hardly offered any space. In order to be able to install the new encoder, the board layout had to be changed and a new additional board designed for the new encoder. After a while I received the additional board with the new encoder. The installation was not easy to do. Part of the existing board had to be cut off. This can be seen from the red marking on the third picture. This was best done with a cutter, a so-called box knife. The next adjustment had to be soldered. The board connection between the display board and the main board had to be changed. It had to be shorter so that the new encoder could even fit. The axis bushing on the housing also had to be drilled out. After the conversion, which took about an hour, I was finally able to put the new encoder into operation. This feels very different from the old mechanical encoder. The new optical tuning encoder turns silky smooth and precisely. Because the diameter of the axis was 6.35mm, I had to drill an existing button to the 6.35mm, which can only be done on a lathe or milling bench. The LAN-IQ is now delivered with this encoder and tuning button. The whole thing can still be ordered separately as a special option. Note: The LAN-IQ receivers that will be delivered immediately are optimized for the new optical encoder. If you buy a newer device without an encoder and want to retrofit the encoder, you no longer have to cut the board. Nevertheless, it is recommended to leave the upgrade with the new encoder to a professional. It is best to order the special option. In addition to the optical encoder, a lot of software updates were made. After my first test, I sent Alexander a list of suggestions for improvement. Because the LAN-IQ is also being discussed in the Groups.io forum, some suggestions came from there to improve the software for standalone operation. Below is a list of the features and improvements that have been made. The list is not exhaustive. Because there are improvements and partly new functions.
The new software updates for standalone operation let the LAN-IQ appear in a completely different light. At first everything was geared towards the radio amateur. Now the LAN-IQ can be used universally and is even more pleasant to use. Especially when you order the optical encoder, which I definitely recommend. A great update is the extension of the RTTY decoder. This now also allows the decoding of professional sea weather reports from DWD and others. FT8 has also been added, an operating mode that is particularly interesting for radio amateurs. A Morse decoder was also implemented. Unfortunately, it doesn't work very well and should be viewed as an encore. New, sensible bandwidths have been added for VHF reception, which also enable VHF DX. The most important functions can best be described and demonstrated with a video.
Conclusion:
With the new functions
and updates for standalone operation, the LAN-IQ is a serious SDR
receiver and can now finally be used universally. Radio listeners
will be happy about the new bandwidth filters for AM and SAM with
selectable sidebands. The new optical encoder was a good decision by
the developer, which considerably enhances the LAN-IQ. However,
there are still a few weak points that could be corrected with
software updates. The RTTY and the CW decoder afford one or the
other error in the decoding. The memory functions should also be
optimized so that when the memory is switched through, the device
immediately switches to the frequency. In my opinion, what is still
missing from the LAN-IQ is a Navtex decoder, a simple scan function
for the upper bands and an adjustable noise blanker. These things
were already under discussion but not yet implemented. Hopefully
this will still happen. Then the LAN-IQ would also be fully usable
in the maritime sector. posted: 02.12.2020
|
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)













.jpg)
.jpg)
001.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)